Phishing is a fraudulent activity that aims to steal user credentials, credit card and bank account information or to deploy malicious software on the victim’s infrastructure. For instance, fraudster can massively send letters containing malicious links, by clicking on which the user allows the attacker to get sensitive data. There are various phishing URL detection techniques: white/black lists usage, heuristics oriented approaches such as usage of content, visual and URL features. Here we will discuss URL-based method using standard machine learning approaches (Logistic regression, Random forest, Stochastic gradient descent classifier and etc.) in combination with NLP driven features which can be extracted from the URL.

- Introduction
- Dataset
- Measuring ML model performance
- Phishing URL detection using ML methods
- Conclusion
Introduction
Machine learning is now widely used in different cybersecurity areas. Among them are the following areas:
- malware detection and classification;
- domain generation algorithms and botnet detection;
- network intrusion detection;
- URL detection;
- spam filtering;
- malicious insiders threats;
- cyber-physical systems (CPS) and industrial control systems (ICS);
- biometric systems (face recognition, speaker verification/recognition, fingerprint systems);
- anomalous user behaviour analysis and etc.
In this tutorial we will consider only one of these numerous cases and will give some insights how by combining NLP features and standard (non-deep learning) machine learning algorithms perform the detection of phishing URLs.
There are different types of URL obfuscation:
| Type | Sample |
|---|---|
| Obfuscation with other domains | http://school497.ru/222/www.paypal.com/29370274276105805 |
| Obfuscation with keywords | http://quadrodeofertas.com.br/www1.paypal-com/encrypted/ssl218 |
| Typo-squatting domains | http://cgi-3.paypal-secure.de/info2/verikerdit.html |
| Obfuscation with IP address | http://69.72.130.98/javaseva/https://paypal.com/uk/onepagepaypal.htm |
| Obfuscation with URL shorteners | http://goo.gl/HQx5g |
Common features for phishing URL detection:
| Feature name | Description |
|---|---|
| IP address | Check if IP address is presented in existing domains |
| Avg. words length | Count average length of meaningful words in entire domain name |
| exe/zip | Check if exe/zip is present in URL |
| No of dots | Count # of dots in URL |
| Special symbols | Count special symbols in URL |
| URL length | Count # of in URL |
| Top-level domain (TLD) feature | Validate TLD-based features |
| “http” count | Count # of “http” in URL |
| “//” redirection | Check if “//” is included in URL path |
| Domain separated by “-“ | Check if “-“ is included in domain name |
| Multi-sub domain | Check how many # of multi-subdomains are included in URL |
| Suspicious words | Check if suspicious words are included in URL |
| Digits in domain | # of digits in domain |
| Character entropy | Calculate character distribution in entire URL using entropy |
| Shorten URL | Check if URL is shortened |
Dataset
In this tutorial I used Kaggle dataset “Phishing Site URLs” which contains 549346 entries of URLs labeled with 2 categories (“Good”, “Bad”).
It is also an interesting fact that you can use this site to view cyberattacks in a real time.
Other datasets from Kaggle containing legitimate/malicious URLs:
- Web page Phishing Detection Dataset (11430 URLs with 87 extracted features);
- Malicious URLs dataset (651191 URLs, out of which 428103 benign or safe URLs, 96457 defacement URLs, 94111 phishing URLs, and 32520 malware URLs);
- Raw Url dataset (raw Legitimate and phishing URLs, without labeling);
- A comprehensive dataset for Malicious Attacks (contains legitimate and phishing URLs with labels).
Datasets for vision based approaches (images):
- Phish-Iris Dataset (involves 1313 training and 1539 testing images samples);
Also researchers collect data sources from popular websites such as Alexa and DMOZ for legitimate, and PhishTank and OpenPhish for phishing. There are common sources to collect your own dataset:
| Type | Data source |
|---|---|
| Legitimate | digg58.com, Alexa, DMOZ, payment gateway, Top banking website |
| Phishing | PhishTank, OpenPhish, VirusTotal, MalewareDomainList, MalewareDomains, jwSpamSpy |
Measuring ML model performance
Important metrics for measuring the quality of cybersecurity machine learning models are precision and recall. Let’s look at their meaning in the light of cybesecurity. Here is their formulas:
\[Precision = \frac{TP}{TP + FP}\] \[Recall = \frac{TP}{TP + FN}\]- TP (True Positives) here is the number of relevant samples which actually have positive class after algorithm application (sick people correctly identified as sick).
- FP (False Positives) determines type I error where relevant samples with positive classes were classified as negative ones (healthy people incorrectly identified as sick).
- FN (False Negatives) is a type II error which determines relevant samples with negative class classified as positive (sick people incorrectly identified as healthy).
In cyber security case recall metric is critical bacause it determines the rate of malicious samples we have passed as legitimate, so FN should be as lowest as possible. Precision metrics will act like the friction rate for legitimate users, for instance, we block https://www.kaggle.com/ URL which is also not good practice. In cybersecurity applications there should be always optimal trade-off between recall and precision.
Phishing URL detection using ML methods
Kaggle dataset import
I used Google Colab environment to calculate this notebook, using Colab notebook you can simply import any Kaggle dataset using your Kaggle credentials. To do so, you need to install kaggle library into created Colab environment.
In [1]:
!pip install kaggleThen go to your profile on Kaggle site (if you are registered user), toggle the “Account” tab and in section “API” click “Create New API Token” button and download your API credentials in json file. This file will be named “kaggle.json”, load it in appeared form after following command execution
In [2]:
from google.colab import files
files.upload()In [3]:
!mkdir -p ~/.kaggle
!cp kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/
!chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.jsonCopy API command from here and paste it in the cell below:
In [4]:
!kaggle datasets download -d taruntiwarihp/phishing-site-urlsOut [4]:
Downloading phishing-site-urls.zip to /content
0% 0.00/9.03M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100% 9.03M/9.03M [00:00<00:00, 77.9MB/s]
So now, Kaggle dataset successfully downloaded into Colab environment, let’s unzip it:
In [5]:
import zipfile
zip_ref = zipfile.ZipFile('phishing-site-urls.zip', 'r')
zip_ref.extractall()
zip_ref.close()In [6]:
import re
import os
import string
import random
import pickle
import warnings
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix, hstack
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
pd.set_option("display.max_colwidth", 999)
SEED = 2021In [7]:
def seed_everything(seed=1234):
random.seed(seed)
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
seed_everything(SEED)Let’s load imported data into the memory and perform some standard Exploratory Data Analysis.
In [8]:
data = pd.read_csv('/content/phishing_site_urls.csv')EDA
In [9]:
data.head()Out [9]:
| URL | Label | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | nobell.it/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782/login.SkyPe.com/en/cgi-bin/verification/login/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373/index.php?cmd=_profile-ach&outdated_page_tmpl=p/gen/failed-to-load&nav=0.5.1&login_access=1322408526 | bad |
| 1 | www.dghjdgf.com/paypal.co.uk/cycgi-bin/webscrcmd=_home-customer&nav=1/loading.php | bad |
| 2 | serviciosbys.com/paypal.cgi.bin.get-into.herf.secure.dispatch35463256rzr321654641dsf654321874/href/href/href/secure/center/update/limit/seccure/4d7a1ff5c55825a2e632a679c2fd5353/ | bad |
| 3 | mail.printakid.com/www.online.americanexpress.com/index.html | bad |
| 4 | thewhiskeydregs.com/wp-content/themes/widescreen/includes/temp/promocoessmiles/?84784787824HDJNDJDSJSHD//2724782784/ | bad |
In [10]:
print(f"There are {data['URL'].duplicated().sum()} duplicated URLs in the data")
data.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)Out [10]:
There are 42151 duplicated URLs in the data
In [11]:
data.isna().sum()Out [11]:
URL 0
Label 0
dtype: int64
In [12]:
data.info()Out [12]:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 507196 entries, 0 to 516470
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 URL 507196 non-null object
1 Label 507196 non-null object
dtypes: object(2)
memory usage: 11.6+ MB
In the field of cybersecurity, malicious incidents are less common than legitimate ones. Thus, by performing your machine learning algorithm you should take into account class imbalance.
In [13]:
ax = sns.catplot("Label",
data=data,
kind="count",
palette='tab20');Out [13]:
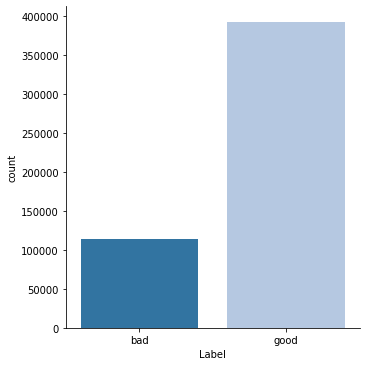
Feature engineering/Data preprocessing
Here is the general structure of any URL, you can simply write regex expression to extract interesting parts of the URL like I did below. Function url_path_to_dict extracts protocol, username, password, hostname, port, path and query. These features we will use for our linguistic patterns.
In [14]:
def url_path_to_dict(path):
pattern = (r'^'
r'((?P<schema>.+?)://)?'
r'((?P<user>.+?)(:(?P<password>.*?))?@)?'
r'(?P<host>.*?)'
r'(:(?P<port>\d+?))?'
r'(?P<path>/.*?)?'
r'(?P<query>[?].*?)?'
r'$'
)
regex = re.compile(pattern)
m = regex.match(path)
d = m.groupdict() if m is not None else None
return d
url = data['URL'].iloc[0]
print(url)
print(url_path_to_dict(url))Out [14]:
nobell.it/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782/login.SkyPe.com/en/cgi-bin/verification/login/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373/index.php?cmd=_profile-ach&outdated_page_tmpl=p/gen/failed-to-load&nav=0.5.1&login_access=1322408526
{'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'nobell.it', 'port': None, 'path': '/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782/login.SkyPe.com/en/cgi-bin/verification/login/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373/index.php', 'query': '?cmd=_profile-ach&outdated_page_tmpl=p/gen/failed-to-load&nav=0.5.1&login_access=1322408526'}
Following helper functions are used to extract NLP features from the URL:
In [15]:
VOWELS = set("aeiou")
CONSONANTS = set(string.ascii_lowercase) - set("aeiou")
def url_length(s: str):
return len(s)
def hostname_length(d: dict):
if not d:
return 0
if not d['host']:
return 0
else:
return len(d['host'])
def path_length(d: dict):
if not d:
return 0
if not d['path']:
return 0
else:
return len(d['path'])
def query_length(d: dict):
if not d:
return 0
if not d['query']:
return 0
else:
return len(d['query'])
def is_ip(d:dict):
if not d:
return False
res_s = re.sub(r'[/.]', '', d['host'])
return int(res_s.isnumeric())
def contains_port(d:dict):
if not d:
return False
if d['port']:
return 1
else:
return 0
def contains_username(d:dict):
if not d:
return False
if d['user']:
return 1
else:
return 0
def vowels_pct(s):
count = 0
s = s.lower()
for ch in s:
if ch in VOWELS:
count = count + 1
return count/len(s)
def consonants_pct(s):
count = 0
s = s.lower()
for ch in s:
if ch in CONSONANTS:
count = count + 1
return count/len(s)
def count_dots(s):
return s.count('.')
def count_slash(s):
return s.count('/')
def count_digits(s):
return len(re.sub(r"\D", "", s))
def count_punctuation(s):
return len(re.sub(r"[^" + string.punctuation + "]+", "", s))
def extract_doc(s):
return " ".join(re.split("[" + string.punctuation + "]+", s))Function extract_doc splits URL by punctuation signs and join its tokens with a space character. For example, you have the following link: www.dghjdgf.com/paypal.co.uk/cycgi-bin/webscrcmd=_home-customer&nav=1/loading.php
After extract_doc function application to this link you will get the following string: www dghjdgf com paypal co uk cycgi bin webscrcmd home customer nav 1 loading php
In [16]:
%%time
data['url_info'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: url_path_to_dict(x))
data['doc'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: extract_doc(x))
data['vowels_pct'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: vowels_pct(x))
data['consonants_pct'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: consonants_pct(x))
data['is_ip'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: is_ip(x))
data['contains_port'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: contains_port(x))
data['contains_username'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: contains_username(x))
data['url_length'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: url_length(x))
data['dots_num'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: count_dots(x))
data['slash_num'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: count_slash(x))
data['digits_num'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: count_digits(x))
data['punct_num'] = data['URL'].apply(lambda x: count_punctuation(x))
data['host_length'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: hostname_length(x))
data['path_length'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: path_length(x))
data['query_length'] = data['url_info'].apply(lambda x: query_length(x))Out [16]:
CPU times: user 22.2 s, sys: 142 ms, total: 22.3 s
Wall time: 22.3 s
Here what we got after feature engineering pipeline application:
In [17]:
data.head()Out [17]:
| URL | Label | url_info | doc | vowels_pct | consonants_pct | is_ip | contains_port | contains_username | url_length | dots_num | slash_num | digits_num | punct_num | host_length | path_length | query_length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | nobell.it/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782/login.SkyPe.com/en/cgi-bin/verification/login/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373/index.php?cmd=_profile-ach&outdated_page_tmpl=p/gen/failed-to-load&nav=0.5.1&login_access=1322408526 | bad | {'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'nobell.it', 'port': None, 'path': '/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782/login.SkyPe.com/en/cgi-bin/verification/login/70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373/index.php', 'query': '?cmd=_profile-ach&outdated_page_tmpl=p/gen/failed-to-load&nav=0.5.1&login_access=1322408526'} | nobell it 70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373782 login SkyPe com en cgi bin verification login 70ffb52d079109dca5664cce6f317373 index php cmd profile ach outdated page tmpl p gen failed to load nav 0 5 1 login access 1322408526 | 0.204444 | 0.395556 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 225 | 6 | 10 | 58 | 32 | 9 | 125 | 91 |
| 1 | www.dghjdgf.com/paypal.co.uk/cycgi-bin/webscrcmd=_home-customer&nav=1/loading.php | bad | {'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'www.dghjdgf.com', 'port': None, 'path': '/paypal.co.uk/cycgi-bin/webscrcmd=_home-customer&nav=1/loading.php', 'query': None} | www dghjdgf com paypal co uk cycgi bin webscrcmd home customer nav 1 loading php | 0.209877 | 0.592593 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 81 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 15 | 15 | 66 | 0 |
| 2 | serviciosbys.com/paypal.cgi.bin.get-into.herf.secure.dispatch35463256rzr321654641dsf654321874/href/href/href/secure/center/update/limit/seccure/4d7a1ff5c55825a2e632a679c2fd5353/ | bad | {'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'serviciosbys.com', 'port': None, 'path': '/paypal.cgi.bin.get-into.herf.secure.dispatch35463256rzr321654641dsf654321874/href/href/href/secure/center/update/limit/seccure/4d7a1ff5c55825a2e632a679c2fd5353/', 'query': None} | serviciosbys com paypal cgi bin get into herf secure dispatch35463256rzr321654641dsf654321874 href href href secure center update limit seccure 4d7a1ff5c55825a2e632a679c2fd5353 | 0.214689 | 0.412429 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 177 | 7 | 11 | 47 | 19 | 16 | 161 | 0 |
| 3 | mail.printakid.com/www.online.americanexpress.com/index.html | bad | {'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'mail.printakid.com', 'port': None, 'path': '/www.online.americanexpress.com/index.html', 'query': None} | mail printakid com www online americanexpress com index html | 0.300000 | 0.566667 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 18 | 42 | 0 |
| 4 | thewhiskeydregs.com/wp-content/themes/widescreen/includes/temp/promocoessmiles/?84784787824HDJNDJDSJSHD//2724782784/ | bad | {'schema': None, 'user': None, 'password': None, 'host': 'thewhiskeydregs.com', 'port': None, 'path': '/wp-content/themes/widescreen/includes/temp/promocoessmiles/', 'query': '?84784787824HDJNDJDSJSHD//2724782784/'} | thewhiskeydregs com wp content themes widescreen includes temp promocoessmiles 84784787824HDJNDJDSJSHD 2724782784 | 0.198276 | 0.508621 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 116 | 1 | 10 | 21 | 13 | 19 | 60 | 37 |
In [18]:
data['Label'] = data.Label.apply(lambda x: 0 if x=='bad' else 1)In [19]:
folds = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=SEED)
X = data.iloc[:, 3:]
y = data.Label.valuesIn [20]:
tf_idf_vec = TfidfVectorizer(encoding='utf-8',
stop_words='english',
ngram_range=(1, 3),
max_df=0.8, min_df=1000)
sc = RobustScaler(with_centering=True, with_scaling=True, quantile_range=(25.0, 75.0), copy=True)In [21]:
NOT_SCALE_COLUMNS = ["vowels_pct", "consonants_pct", "is_ip", "contains_port", "contains_username"]
TO_SCALE_COLUMNS = ["url_length", "dots_num", "slash_num", "digits_num", "punct_num", "host_length", "path_length", "query_length"]
GOOD_SAMPLES = ['youtube.com/',
'youtube.com/watch?v=qI0TQJI3vdU',
'bestbuy.com/',
'restorevisioncenters.com/html/technology.html',
'mariazork.github.io/CodingProblems']
BAD_SAMPLES = ['http://shadetreetechnology.com/V4/validation/a111aedc8ae390eabcfa130e041a10a4',
'yeniik.com.tr/wp-admin/js/login.alibaba.com/login.jsp.php',
'fazan-pacir.rs/temp/libraries/ipad',
'tubemoviez.exe',
'svision-online.de/mgfi/administrator/components/com_babackup/classes/fx29id1.txt']In [22]:
def preprocess(Xtrain, Xval, vectorizer, scaler, fold_index):
Xtrain_vect = vectorizer.fit_transform(Xtrain.doc.values)
Xtrain_num = scaler.fit_transform(Xtrain.loc[:, TO_SCALE_COLUMNS].values)
Xtrain_num = coo_matrix(Xtrain_num)
Xtrain_num_add = coo_matrix(Xtrain.loc[:, NOT_SCALE_COLUMNS].values).astype('float32')
Xtrain_res = hstack([Xtrain_vect, Xtrain_num_add, Xtrain_num])
Xtrain_res = Xtrain_res.astype('float32')
Xval_vect = vectorizer.transform(Xval.doc.values)
Xval_num = scaler.transform(Xval.loc[:, TO_SCALE_COLUMNS].values)
Xval_num = coo_matrix(Xval_num)
Xval_num_add = coo_matrix(Xval.loc[:, NOT_SCALE_COLUMNS].values).astype('float32')
Xval_res = hstack([Xval_vect, Xval_num_add, Xval_num])
Xval_res = Xval_res.astype('float32')
pickle.dump(vectorizer, open(f"tf_idf_{fold_index}.pkl", "wb"))
pickle.dump(scaler, open(f"scaler_{fold_index}.pkl", "wb"))
return Xtrain_res, Xval_res
def train(model, X, y, vectorizer, scaler):
precision_scores, recall_scores = [], []
for fold_idx, (train_index, val_index) in enumerate(folds.split(X, y)):
X_train, X_val = X.iloc[train_index, :], X.iloc[val_index, :]
y_train, y_val = y[train_index], y[val_index]
X_train_, X_val_ = preprocess(X_train, X_val, vectorizer, scaler, fold_idx)
model.fit(X_train_, y_train)
y_hat = model.predict(X_val_)
precision_scores.append(precision_score(y_val, y_hat))
recall_scores.append(recall_score(y_val, y_hat))
pickle.dump(model, open(f"model_{fold_idx}.pkl", "wb"))
return precision_scores, recall_scores
def infer(sample: np.array,
model_filename: str,
vectorizer_filename: str,
scaler_filename: str):
model = pickle.load(open(model_filename, "rb"))
tf_idf_vec = pickle.load(open(vectorizer_filename, "rb"))
sc = pickle.load(open(scaler_filename, "rb"))
feature_vec = np.array([])
url_info = url_path_to_dict(sample)
doc = extract_doc(sample)
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, tf_idf_vec.transform(np.array([doc])).toarray())
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, vowels_pct(sample))
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, consonants_pct(sample))
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, is_ip(url_info))
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, contains_port(url_info))
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec, contains_username(url_info))
feature_vec = np.append(feature_vec,
sc.transform(np.array([[url_length(sample),
count_dots(sample),
count_slash(sample),
count_digits(sample),
count_punctuation(sample),
hostname_length(url_info),
path_length(url_info),
query_length(url_info)]])))
y_hat = model.predict(feature_vec.reshape(1, -1))
return y_hatLogistic regression
In [23]:
lr = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2',
tol=0.0001,
C=0.01,
class_weight='balanced',
random_state=SEED,
solver='lbfgs',
max_iter=100,
n_jobs=-1)
precision_scores, recall_scores = train(lr, X, y, tf_idf_vec, sc)
print("==Logistic regression results==")
print("Precision scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, precision_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Recall scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, recall_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Mean recall over folds", np.mean(recall_scores))
print("Std of recall over folds", np.std(recall_scores))
print("Mean precision over folds", np.mean(precision_scores))
print("Std of precision over folds", np.std(precision_scores))Out [23]:
==Logistic regression results==
Precision scores:
0.93784306550264
0.9394603245398854
0.9352301342125074
0.9387226358556979
0.9379541570453863
====================
Recall scores:
0.91320946805803
0.911388538922613
0.9169370951526489
0.9129665686761094
0.9149529142275388
====================
Mean recall over folds 0.913890917007388
Std of recall over folds 0.0018967196933418495
Mean precision over folds 0.9378420634312233
Std of precision over folds 0.0014303088503269622
In [24]:
answers = []
for sample in GOOD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [24]:
[array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1])]
Here we can see that fazan-pacir.rs/temp/libraries/ipad URL was classified as legitimate by Logistic regression algorithm.
In [25]:
answers = []
for sample in BAD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [25]:
[array([0]), array([0]), array([1]), array([0]), array([0])]
SGD Classifier
In [26]:
sgd = SGDClassifier(random_state=SEED,
class_weight='balanced',
n_jobs=-1)
precision_scores, recall_scores = train(sgd, X, y, tf_idf_vec, sc)
print("==SGD classifier results==")
print("Precision scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, precision_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Recall scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, recall_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Mean recall over folds", np.mean(recall_scores))
print("Std of recall over folds", np.std(recall_scores))
print("Mean precision over folds", np.mean(precision_scores))
print("Std of precision over folds", np.std(precision_scores))Out [26]:
==SGD classifier results==
Precision scores:
0.9341991999594916
0.9406067274844224
0.9423525535420099
0.9426472102120651
0.9424178044925772
====================
Recall scores:
0.9391448205650292
0.9355553010346276
0.9099250435867089
0.9322465289708446
0.9257953677780606
====================
Mean recall over folds 0.9285334123870541
Std of recall over folds 0.010290426775929541
Mean precision over folds 0.9404446991381132
Std of precision over folds 0.003206762272833252
SGD classifier made a mistake with mariazork.github.io/CodingProblems URL and classified it as malicious.
In [27]:
answers = []
for sample in GOOD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [27]:
[array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([0])]
But there is no mistakes for malicious samples.
In [28]:
answers = []
for sample in BAD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [28]:
[array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0])]
Random forest
In [29]:
rf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=100,
random_state=SEED,
class_weight='balanced',
n_jobs=-1)
precision_scores, recall_scores = train(rf, X, y, tf_idf_vec, sc)
print("==Random forest results==")
print("Precision scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, precision_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Recall scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, recall_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Mean recall over folds", np.mean(recall_scores))
print("Std of recall over folds", np.std(recall_scores))
print("Mean precision over folds", np.mean(precision_scores))
print("Std of precision over folds", np.std(precision_scores))Out [29]:
==Random forest results==
Precision scores:
0.9654844323146838
0.9651363306925249
0.9635700820234959
0.9653545868575146
0.9646089608960896
====================
Recall scores:
0.981420208704505
0.9829089196859212
0.9822089871339671
0.9818781099275888
0.9819419699669127
====================
Mean recall over folds 0.9820716390837789
Std of recall over folds 0.000489598293873607
Mean precision over folds 0.9648308785568618
Std of precision over folds 0.0006976473682924858
Random forest has shown best performance and the is no mistakes in both classes detection.
In [30]:
answers = []
for sample in GOOD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [30]:
[array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1])]
In [31]:
answers = []
for sample in BAD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [31]:
[array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0])]
Linear SVM
In [32]:
linear_svm = LinearSVC(random_state=SEED,
class_weight='balanced')
precision_scores, recall_scores = train(linear_svm, X, y, tf_idf_vec, sc)
print("==Support Vector Machines results==")
print("Precision scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, precision_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Recall scores:\n", "\n".join(map(str, recall_scores)))
print("="*20)
print("Mean recall over folds", np.mean(recall_scores))
print("Std of recall over folds", np.std(recall_scores))
print("Mean precision over folds", np.mean(precision_scores))
print("Std of precision over folds", np.std(precision_scores))Out [32]:
==Support Vector Machines results==
Precision scores:
0.9531297649195847
0.9549273129228915
0.9496824749858659
0.950237309527879
0.9489986333052985
====================
Recall scores:
0.9148129294986002
0.9069980529149009
0.9192023314117004
0.9197877295460619
0.918999745482311
====================
Mean recall over folds 0.9159601577707148
Std of recall over folds 0.004817396500707926
Mean precision over folds 0.9513950991323039
Std of precision over folds 0.0022584156548811265
In [33]:
answers = []
for sample in GOOD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [33]:
[array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([1]), array([0])]
In [34]:
answers = []
for sample in BAD_SAMPLES:
answers.append(infer(sample, "model_0.pkl", "tf_idf_0.pkl", "scaler_0.pkl"))
print(answers)Out [34]:
[array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0]), array([0])]
Conclusion
| Algorithm | Mean Precision over 5 folds | Mean Recall over 5 folds |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic regression | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| SGD classifier | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| Random Forest | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| Linear SVM | 0.95 | 0.92 |